
See: Description
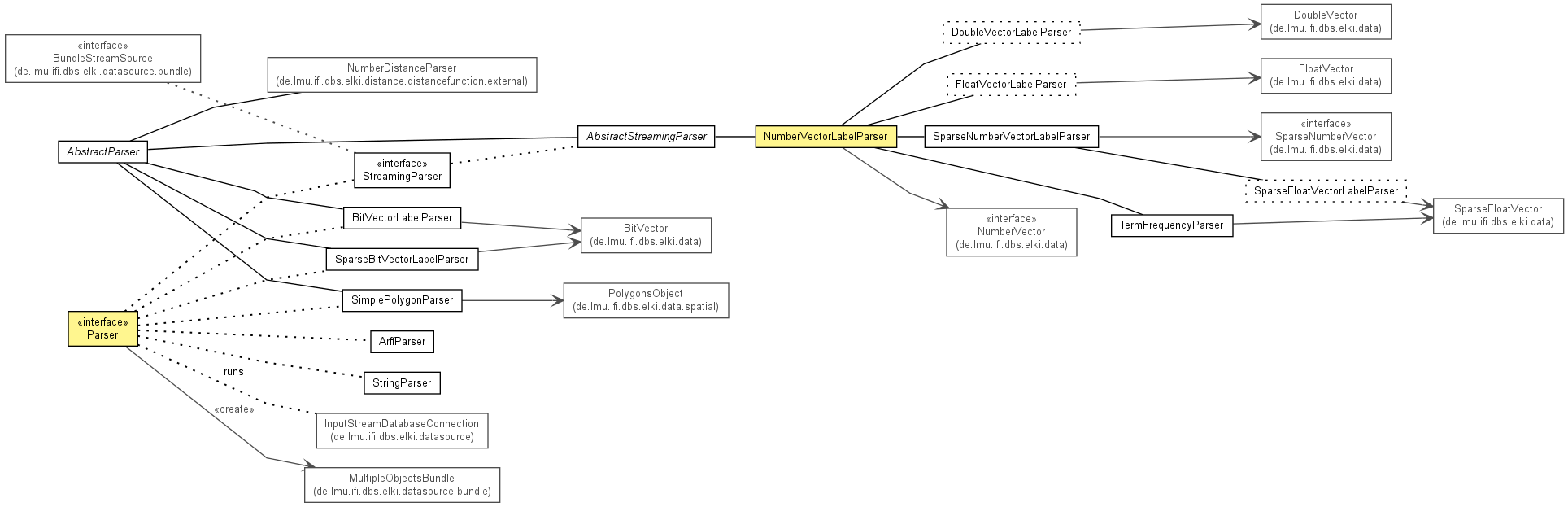
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Parser |
A Parser shall provide a ParsingResult by parsing an InputStream.
|
| StreamingParser |
Interface for streaming parsers, that may be much more efficient in
combination with filters.
|
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| AbstractParser |
Abstract superclass for all parsers providing the option handler for handling
options.
|
| AbstractParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| AbstractStreamingParser |
Base class for streaming parsers.
|
| ArffParser |
Parser to load WEKA .arff files into ELKI.
|
| ArffParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| BitVectorLabelParser |
Provides a parser for parsing one BitVector per line, bits separated by
whitespace.
|
| BitVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| DoubleVectorLabelParser | Deprecated
Use NumberVectorLabelParser instead, which defaults to
DoubleVector.
|
| DoubleVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| FloatVectorLabelParser | Deprecated
Use NumberVectorLabelParser instead, and use vector type FloatVector.
|
| FloatVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| NumberVectorLabelParser<V extends NumberVector<?>> |
Provides a parser for parsing one point per line, attributes separated by
whitespace.
|
| NumberVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer<V extends NumberVector<?>> |
Parameterization class.
|
| SimplePolygonParser |
Parser to load polygon data (2D and 3D only) from a simple format.
|
| SimplePolygonParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| SparseBitVectorLabelParser |
Provides a parser for parsing one sparse BitVector per line, where the
indices of the one-bits are separated by whitespace.
|
| SparseBitVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| SparseFloatVectorLabelParser | Deprecated
Use
SparseNumberVectorLabelParser instead! |
| SparseFloatVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| SparseNumberVectorLabelParser<V extends SparseNumberVector<?>> |
Provides a parser for parsing one point per line, attributes separated by
whitespace.
|
| SparseNumberVectorLabelParser.Parameterizer<V extends SparseNumberVector<?>> |
Parameterization class.
|
| StringParser |
Parser that loads a text file for use with string similarity measures.
|
| StringParser.Parameterizer |
Parameterization class.
|
| TermFrequencyParser<V extends SparseNumberVector<?>> |
A parser to load term frequency data, which essentially are sparse vectors
with text keys.
|
| TermFrequencyParser.Parameterizer<V extends SparseNumberVector<?>> |
Parameterization class.
|
Parsers for different file formats and data types.
The general use-case for any parser is to create objects out of an
InputStream (e.g. by reading a data file).
The objects are packed in a
MultipleObjectsBundle which,
in turn, is used by a DatabaseConnection-Object
to fill a Database
containing the corresponding objects.
By default (i.e., if the user does not specify any specific requests),
any KDDTask will
use the StaticArrayDatabase which,
in turn, will use a FileBasedDatabaseConnection
and a DoubleVectorLabelParser
to parse a specified data file creating
a StaticArrayDatabase
containing DoubleVector-Objects.
Thus, the standard procedure to use a data set of a real-valued vector space
is to prepare the data set in a file of the following format
(as suitable to DoubleVectorLabelParser):
As an example file following these requirements consider e.g.: exampledata.txt